What Is The Roman Numeral For 100
lube
Dec 04, 2025 · 13 min read
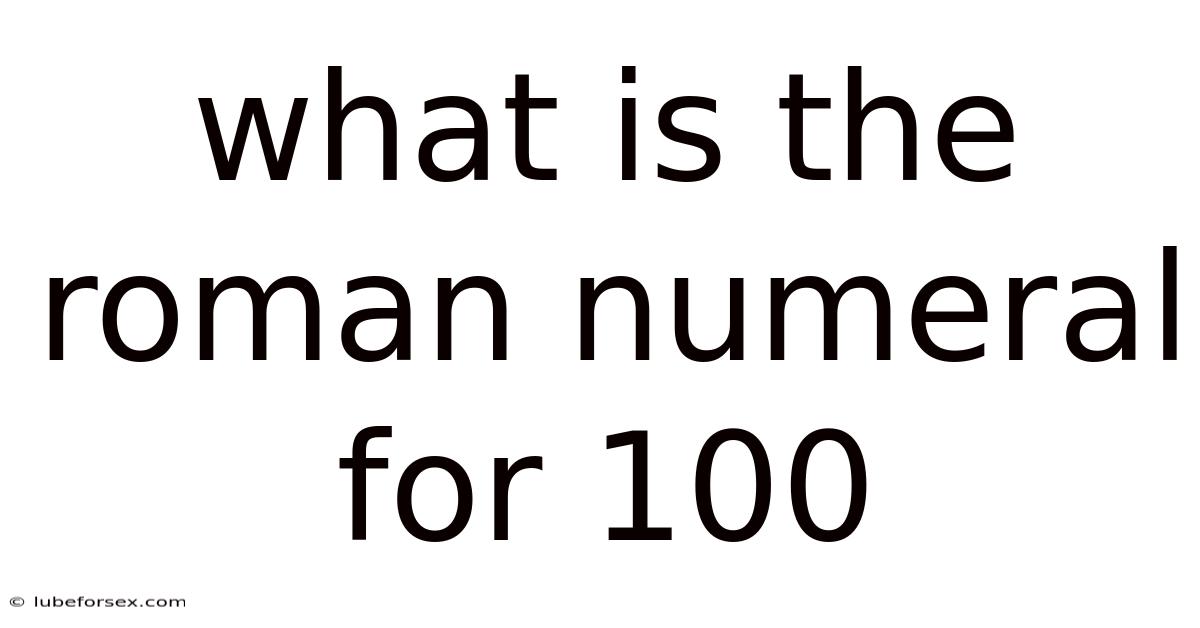
Table of Contents
Imagine stumbling upon an ancient manuscript, its yellowed pages filled with cryptic symbols. Among them, you spot a symbol that looks like a simple capital "C." But this isn't just any letter; it's a Roman numeral, a relic from a civilization that once ruled a vast empire. The symbol "C" represents 100, a foundational number in the Roman numeral system, and understanding its significance unlocks a gateway to appreciating the mathematical prowess and historical context of the Roman world.
From the grand Colosseum to the intricate aqueducts, Roman numerals were integral to the empire's identity, marking everything from dates on cornerstones to quantities of goods traded in the bustling marketplaces. The Roman numeral system, while different from our modern Arabic numerals, served its purpose effectively for centuries. Knowing that "C" stands for 100 is just the beginning. Delving into the Roman numeral system reveals a fascinating approach to representing numbers, one that combines simplicity with a clever use of additive and subtractive principles. So, let's explore the world of Roman numerals, understand why "C" signifies 100, and appreciate the lasting impact of this ancient numbering system.
Main Subheading
The Roman numeral system, a method of numerical notation used by the ancient Romans, relies on a set of symbols to represent numbers. Unlike the positional number system we use today (the Arabic numeral system), Roman numerals are additive and subtractive. This means that the value of a numeral is determined by adding or subtracting the values of the symbols. The system uses letters from the Latin alphabet to represent different values, and these values are combined to form larger numbers.
At its core, the Roman numeral system utilizes a limited set of symbols, each with a specific numerical value. The primary symbols are:
- I = 1
- V = 5
- X = 10
- L = 50
- C = 100
- D = 500
- M = 1000
Understanding that C represents 100 is crucial, but it's equally important to grasp how these symbols combine to create other numbers. For instance, II represents 2 (1+1), while VI represents 6 (5+1). The order of the symbols matters significantly, as it determines whether the values are added or subtracted. This system, while seemingly simple, allowed the Romans to perform calculations, record dates, and inscribe numbers on monuments and documents, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to influence our world today.
Comprehensive Overview
The Roman numeral system operates on a few key principles that make it both unique and functional. These principles govern how symbols are combined and interpreted to represent different numerical values. Understanding these rules is essential for accurately converting Roman numerals to Arabic numerals, and vice versa.
Additive Principle
The additive principle is one of the most straightforward aspects of the Roman numeral system. When symbols are placed in descending order of value, their values are added together. For example:
- VIII = 5 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 8
- XX = 10 + 10 = 20
- LX = 50 + 10 = 60
- CL = 100 + 50 = 150
- MC = 1000 + 100 = 1100
In each of these examples, the symbols are arranged from highest to lowest value, and their values are simply added to obtain the total numerical value. This principle makes it easy to represent numbers that are sums of the basic numeral values.
Subtractive Principle
The subtractive principle is applied when a symbol of smaller value is placed before a symbol of larger value. In this case, the smaller value is subtracted from the larger value. This rule is used to avoid repeating the same symbol multiple times in a row and to make the numerals more concise. The common subtractive combinations are:
- IV = 5 - 1 = 4
- IX = 10 - 1 = 9
- XL = 50 - 10 = 40
- XC = 100 - 10 = 90
- CD = 500 - 100 = 400
- CM = 1000 - 100 = 900
For instance, rather than writing "IIII" for 4, the Romans used "IV" to represent the same value more efficiently. Similarly, "XC" is used for 90 instead of "LXXXX".
Rules and Limitations
While the additive and subtractive principles provide the foundation for the Roman numeral system, there are specific rules and limitations that govern their application:
- Repetition: A symbol can be repeated up to three times in a row. For example, III = 3, XX = 20, CCC = 300. However, repeating a symbol more than three times is not allowed.
- Subtractive Usage: The symbols I, X, and C can be used as subtractive numerals. The symbol V, L, and D cannot be used subtractively.
- Placement: A subtractive numeral can only be placed before the next two higher numerals. For example, I can be placed before V and X, but not before L or C. Similarly, X can be placed before L and C, but not before D or M.
- Single Subtraction: Only one subtractive numeral is allowed for any given number. For example, 99 should be written as XCIX (100 - 10 + 10 - 1) and not as IC (100 - 1), which is incorrect.
The Significance of "C" = 100
Within the context of these rules, the numeral "C" holds a significant place. Representing 100, "C" is a key component in constructing larger numbers. It is used additively to form numbers like 100 (C), 200 (CC), and 300 (CCC). It is also used subtractively to form numbers like 90 (XC) and 400 (CD).
Historical Context
The Roman numeral system emerged in ancient Rome and was used for centuries, even after the fall of the Roman Empire. Its origins can be traced back to Etruscan numerals, which were adapted and modified by the Romans. The system was primarily used for practical purposes such as commerce, record-keeping, and marking milestones.
While the exact origins of the symbols are debated, some theories suggest that they evolved from tally marks or hand gestures. For example, "I" may have represented a single tally mark, "V" could have symbolized a hand with five fingers, and "X" might have been two "V" symbols placed together. The symbol "C," representing 100, is believed to come from the first letter of the Latin word centum, which means "hundred."
Over time, the Roman numeral system became standardized and widely adopted throughout the Roman world. It played a crucial role in various aspects of Roman life, from inscribing dates on monuments to indicating quantities in trade. Though it was eventually replaced by the more efficient Arabic numeral system, Roman numerals continue to be used in certain contexts, reflecting their enduring historical significance.
Trends and Latest Developments
While the Roman numeral system is ancient, its use persists in modern times, albeit in specific contexts. Trends and adaptations in how Roman numerals are used reflect both a respect for tradition and a need for practical application in contemporary settings.
Modern Usage
Roman numerals are commonly used in the following areas:
- Clock Faces: Many traditional analog clocks and watches use Roman numerals to mark the hours. This adds a touch of elegance and tradition to the design.
- Book Chapters and Prefaces: Publishers often use Roman numerals to number the preliminary pages of books, such as the preface, introduction, or table of contents. They may also be used to number chapters, particularly in older or more formal publications.
- Movie and Game Sequels: Sequels to movies and video games often use Roman numerals to indicate the order of the installment. For example, Rocky II, Grand Theft Auto V.
- Building Cornerstones and Monuments: Roman numerals are frequently used to inscribe dates on building cornerstones, monuments, and plaques. This practice adds a sense of historical significance and permanence to the structure.
- Outlines and Lists: In academic and professional writing, Roman numerals are sometimes used to denote the main sections of an outline or a list.
- Royal Names: Roman numerals are used to distinguish between rulers with the same name. For example, Queen Elizabeth II.
- Super Bowl: The Super Bowl games are numbered with Roman numerals.
Digital Adaptations
Despite the prevalence of Arabic numerals in digital contexts, Roman numerals have found some niches in the digital world:
- HTML and CSS: Web developers can use Roman numerals in ordered lists using HTML and CSS. This allows for the creation of visually distinct lists on websites.
- Digital Clocks and Interfaces: Some digital clocks and user interfaces offer the option to display the time using Roman numerals, catering to users who appreciate the classic aesthetic.
- Educational Software: Roman numerals are often included in educational software and apps designed to teach children about ancient history and mathematics.
Popular Opinions and Misconceptions
There are several popular opinions and misconceptions surrounding Roman numerals:
- Complexity: Some people believe that Roman numerals are inherently more complex and difficult to work with than Arabic numerals. While it is true that performing arithmetic operations with Roman numerals can be challenging, the basic principles of the system are relatively straightforward.
- Limited Use: Some perceive Roman numerals as being outdated and irrelevant in modern society. However, as noted above, they continue to be used in various contexts for aesthetic, historical, or practical reasons.
- Inability to Represent Large Numbers: While the basic Roman numeral system has limitations in representing very large numbers, extensions and modifications were developed to overcome this issue. For example, the vinculum (a horizontal line placed above a numeral) was used to multiply its value by 1,000.
- The perception of "C" solely in the context of copyright: While "C" is universally recognized as the copyright symbol, understanding that "C" also represents 100 in Roman numerals highlights the symbol's multifaceted significance across different domains.
Professional Insights
From a design perspective, Roman numerals offer a unique visual appeal. Their classic and elegant appearance makes them suitable for applications where aesthetics are important, such as clock faces, monuments, and formal documents.
From a historical perspective, the continued use of Roman numerals serves as a tangible link to the past. It reminds us of the achievements and innovations of the Roman civilization and their lasting impact on our world.
Tips and Expert Advice
Working with Roman numerals can be both educational and practical. Here are some tips and expert advice to help you master the system:
Understanding the Basics
Before attempting to convert or use Roman numerals, ensure you have a solid grasp of the basic symbols and their corresponding values:
- I = 1
- V = 5
- X = 10
- L = 50
- C = 100
- D = 500
- M = 1000
Memorizing these values is the first step to becoming proficient with Roman numerals. It is also essential to understand the additive and subtractive principles.
Breaking Down Complex Numerals
When faced with a complex Roman numeral, break it down into smaller, more manageable parts. For example, consider the number MCMXCIV. Instead of trying to decipher the entire numeral at once, break it down as follows:
- M = 1000
- CM = 900 (1000 - 100)
- XC = 90 (100 - 10)
- IV = 4 (5 - 1)
Then, add the values together: 1000 + 900 + 90 + 4 = 1994. This approach simplifies the conversion process and reduces the risk of errors.
Using Online Converters and Resources
Numerous online converters and resources can help you convert between Roman numerals and Arabic numerals. These tools can be particularly useful when dealing with large or complex numbers. Some recommended resources include:
- Online Roman Numeral Converters: Websites like "RapidTables" or "CalculatorSoup" offer free and accurate conversion tools.
- Educational Websites: Sites like "Khan Academy" provide lessons and exercises on Roman numerals.
These resources can serve as valuable aids in learning and working with Roman numerals.
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, proficiency with Roman numerals requires practice. Try converting numbers from Arabic to Roman numerals, and vice versa, on a regular basis. You can create your own exercises or use online quizzes and worksheets. The more you practice, the more comfortable and confident you will become with the system.
Knowing the Common Mistakes
Be aware of common mistakes when working with Roman numerals:
- Incorrect Subtraction: Ensure you only subtract I, X, and C, and that they are placed before the next two higher numerals.
- Exceeding Repetition Limits: Avoid repeating a symbol more than three times in a row.
- Ignoring Order: Always pay attention to the order of the symbols, as it determines whether the values are added or subtracted.
By being mindful of these common pitfalls, you can improve your accuracy and avoid errors.
Appreciating the Historical Context
Understanding the historical context of Roman numerals can enhance your appreciation for the system. Learn about the origins of the numerals, their use in ancient Rome, and their continued presence in modern society. This knowledge can provide a deeper understanding of the significance and relevance of Roman numerals. Remember, "C" doesn't just represent a number; it echoes a civilization.
Applying Roman Numerals in Real-World Scenarios
Look for opportunities to apply your knowledge of Roman numerals in real-world scenarios. For example, try reading the dates on monuments or cornerstones, or deciphering the numbering of Super Bowl games. This practical application will reinforce your understanding and make learning more engaging.
By following these tips and expert advice, you can develop a strong understanding of Roman numerals and confidently use them in various contexts. Whether you are a student, a history enthusiast, or simply curious about ancient numbering systems, mastering Roman numerals can be a rewarding and enriching experience.
FAQ
Q: What is the Roman numeral for 100?
A: The Roman numeral for 100 is C.
Q: How do you write 400 in Roman numerals?
A: 400 is written as CD in Roman numerals. The C (100) is placed before the D (500), indicating subtraction (500 - 100 = 400).
Q: Can you repeat the same Roman numeral more than three times in a row?
A: No, a Roman numeral symbol can only be repeated up to three times in a row. For example, III is valid, but IIII is not. Instead of IIII, you would write IV (5 - 1 = 4).
Q: What are the basic Roman numeral symbols and their values?
A: The basic Roman numeral symbols and their values are:
- I = 1
- V = 5
- X = 10
- L = 50
- C = 100
- D = 500
- M = 1000
Q: How does the subtractive principle work in Roman numerals?
A: The subtractive principle is used when a smaller value is placed before a larger value. In this case, the smaller value is subtracted from the larger value. For example, IV (5 - 1 = 4) and IX (10 - 1 = 9). Only I, X, and C can be used subtractively, and they can only be placed before the next two higher numerals.
Q: Why do we still use Roman numerals today?
A: Roman numerals are used today for various reasons, including historical significance, aesthetic appeal, and practical purposes. They are commonly found on clock faces, in book chapters, in movie sequels, and on building cornerstones.
Q: Is it difficult to learn Roman numerals?
A: Learning Roman numerals is relatively straightforward, especially if you focus on understanding the basic symbols and the additive and subtractive principles. With practice and the use of online resources, most people can become proficient in working with Roman numerals.
Conclusion
Understanding that "C" represents 100 in the Roman numeral system is more than just a mathematical fact; it's a gateway to appreciating the ingenuity and historical significance of ancient Roman civilization. From the additive and subtractive principles to the practical applications that persist today, Roman numerals offer a fascinating glimpse into a different way of representing numbers.
Whether you're deciphering dates on historical monuments, adding a touch of elegance to a design project, or simply satisfying your curiosity about ancient numbering systems, mastering Roman numerals can be a rewarding experience. So, embrace the challenge, practice regularly, and unlock the secrets of this timeless system.
Now that you've explored the world of Roman numerals, why not test your knowledge? Try converting your birthdate into Roman numerals or explore the historical sites in your area and see if you can spot any examples of Roman numerals in use. Share your findings and insights in the comments below and join the conversation!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
You Can Walk A Horse To Water
Dec 04, 2025
-
What Does By Grace Through Faith Mean
Dec 04, 2025
-
What Is The Roman Numeral For 100
Dec 04, 2025
-
What Does A Mean In Python
Dec 04, 2025
-
What Is A Dlc In Gaming
Dec 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Roman Numeral For 100 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.